
In our modern world, TFT displays are everywhere, from our smartphones to our computer monitors and TVs. Yet, for most people, the inner workings of these screens remain a mystery. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of TFT displays, explaining how they work in simple terms that anyone can understand.
What Is a TFT Display?
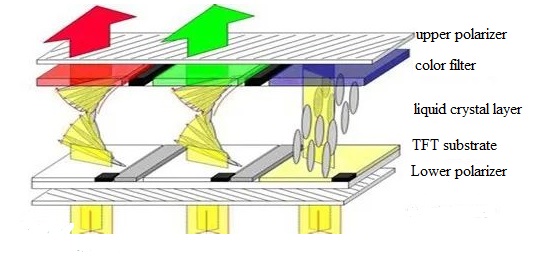
TFT stands for Thin-Film Transistor, and it is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD) technology. Unlike older LCDs, which relied on cumbersome electrical controls, TFT displays use a more advanced method that offers improved image quality and faster response times.
Liquid Crystals: The Heart of the Display
At the core of every TFT display are liquid crystals. These aren't your typical liquid or solid substances but rather a unique state of matter. They flow like a liquid but have the molecular structure of a solid. When an electric current is applied to them, these liquid crystals twist and align themselves in specific ways, allowing or blocking the passage of light.
The Role of Transistors
Now, let's talk about the "Thin-Film Transistors." Each pixel on a TFT display has its own tiny transistor that controls the liquid crystals in that pixel. Think of these transistors as gatekeepers. When the transistor receives an electrical signal, it opens or closes the gate for light to pass through the liquid crystals. This level of control at the pixel level is what gives TFT displays their sharp images and vibrant colors.
Color Production
TFT displays are typically used to produce full-color images. To achieve this, each pixel is further divided into three sub-pixels, one for red, one for green, and one for blue. By varying the intensity of light passing through these sub-pixels, a wide range of colors can be created. When you see a rainbow of colors on your screen, it's these tiny sub-pixels at work.
Backlighting
Behind the liquid crystals and transistors, there's one more critical component: the backlight. TFT displays are not self-illuminating like OLED displays, so they require a light source behind them to make the images visible. This backlight shines through the liquid crystals, creating the bright and vivid images we associate with modern screens.
Conclusion
So, there you have it. The basic principle of how TFT displays work is the controlled manipulation of liquid crystals through thin-film transistors, coupled with backlighting, to produce the images and colors we see on our screens. The next time you gaze at your smartphone or computer monitor, you can appreciate the intricate technology that makes it all possible.